
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
- Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):464-475. Published online March 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0088
- 6,961 View
- 347 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We evaluated the achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) according to up-to-date Korean Diabetes Association (KDA), European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS), and American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines.
Methods
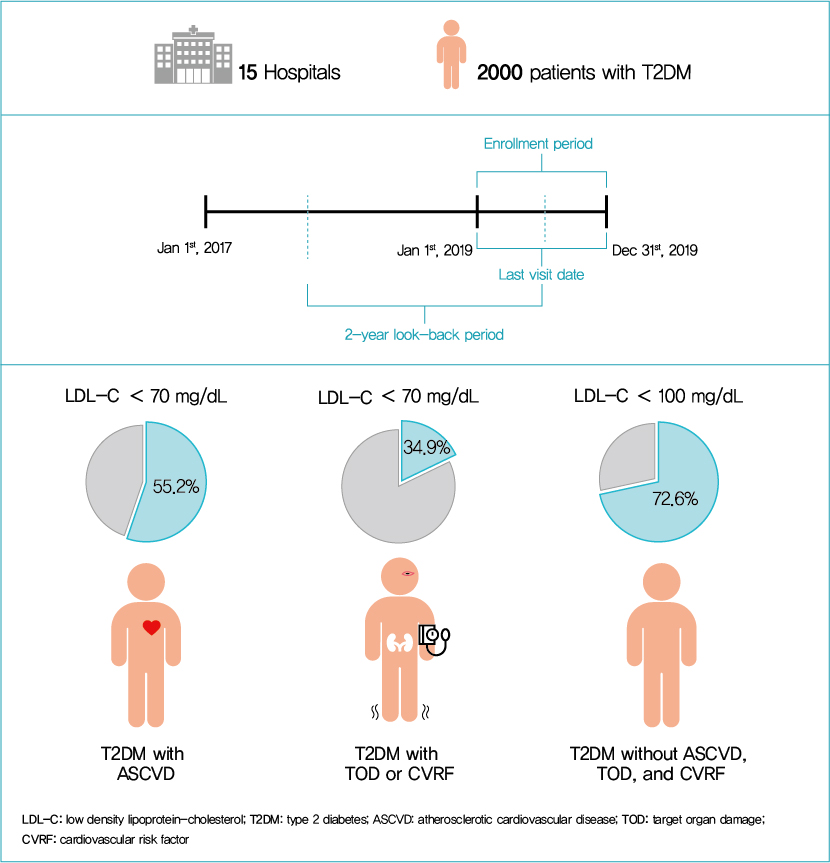
This retrospective cohort study collected electronic medical record data from patients with T2DM (≥20 years) managed by endocrinologists from 15 hospitals in Korea (January to December 2019). Patients were categorized according to guidelines to assess LDL-C target achievement. KDA (2019): Very High-I (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD]) <70 mg/dL; Very High-II (target organ damage [TOD], or cardiovascular risk factors [CVRFs]) <70 mg/dL; high (others) <100 mg/dL. ESC/EAS (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD): <55 mg/dL; Very High-II (TOD or ≥3-CVRF) <55 mg/dL; high (diabetes ≥10 years without TOD plus any CVRF) <70 mg/dL; moderate (diabetes <10 years without CVRF) <100 mg/dL. ADA (2019): Very High-I (ASCVD); Very High-II (age ≥40+ TOD, or any CVRF), for high intensity statin or statin combined with ezetimibe.
Results
Among 2,000 T2DM patients (mean age 62.6 years; male 55.9%; mean glycosylated hemoglobin 7.2%) ASCVD prevalence was 24.7%. Of 1,455 (72.8%) patients treated with statins, 73.9% received monotherapy. According to KDA guidelines, LDL-C target achievement rates were 55.2% in Very High-I and 34.9% in Very High-II patients. With ESC/EAS guidelines, target attainment rates were 26.6% in Very High-I, 15.7% in Very High-II, and 25.9% in high risk patients. Based on ADA guidelines, most patients (78.9%) were very-high risk; however, only 15.5% received high-intensity statin or combination therapy.
Conclusion
According to current dyslipidemia management guidelines, LDL-C goal achievement remains suboptimal in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Hidetaka Hamasaki
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299035. CrossRef - Distinct effects of rosuvastatin and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe on senescence markers of CD8+ T cells in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
Sang-Hyeon Ju, Joung Youl Lim, Minchul Song, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef
- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Women Are Diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes at Higher Body Mass Indices and Older Ages than Men: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2010
- Su Kyoung Kwon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(1):74-80. Published online February 19, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.74
- 3,295 View
- 26 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Many epidemiologic studies have shown that women with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease compared with men with diabetes. The aim of this study is to elucidate whether disparities of adiposity, age and insulin resistance (IR) at the time of diabetes diagnosis exist between women and men in the adult Korean population.
Methods Data from The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, performed in Korea from 2007 to 2010, were used. In the survey, anthropometric data and blood samples were obtained during a fasting state. IR and β-cell function were calculated using the homeostasis model assessment (HOMA-IR and HOMA-β, respectvely).
Results The mean age of diabetes diagnosis was 58.5 years in women and was 55.1 years in men (
P =0.015). The mean body mass index (BMI) of newly diagnosed diabetes subjects was 26.1 kg/m2 in women and 25.0 kg/m2 in men (P =0.001). The BMI was inversely related to age in both genders, and the higher BMI in women than men was consistent throughout all age groups divided by decade. The HOMA-IR in women with diabetes is higher than in men with diabetes (7.25±0.77 vs. 5.20±0.32;P =0.012).Conclusion Korean adult women are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at higher BMI and older age than men and are more insulin-resistant at the time of diabetes diagnosis. This may help explain why women with diabetes have an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease after the diagnosis of diabetes, compared to men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes and cardiovascular risk according to sex: An overview of epidemiological data from the early Framingham reports to the cardiovascular outcomes trials
Abdallah Al-Salameh, Nacera El bouzegaoui, Marie Saraval-Gross
Annales d'Endocrinologie.2023; 84(1): 57. CrossRef - Higher risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in females with type 2 diabetes Mellitus: an Umbrella review of systematic reviews
Clyve Yu Leon Yaow, Bryan Chong, Yip Han Chin, Martin Tze Wah Kueh, Cheng Han Ng, Kai En Chan, Ansel Shao Pin Tang, Charlotte Chung, Rachel Goh, Gwyneth Kong, Mark Muthiah, Indah Sukmawati, Antonia Anna Lukito, Mark Y Chan, Chin Meng Khoo, Anurag Mehta, M
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2023; 30(12): 1227. CrossRef - Indian Phenotype Characteristics Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Insights from a Non-interventional Nationwide Registry in India
Sanjay Kalra, Ambrish Mithal, Abdul Hamid Zargar, Bipin Sethi, Mala Dharmalingam, Sujoy Ghosh, Ranjini Sen
Endocrinology.2022; 18(1): 63. CrossRef - Recreational training improves cardiovascular adaptations, metabolic profile and mental health of elderly women with type-2 diabetes mellitus
Andrea Sanches, Vinicius Guzzoni, Vania C. dos R. Miranda, Laís Bonagurio Peressim, Suellen Rocha, Patrícia Oliveira de Lima, Fernanda Klein Marcondes, Ana Paula Tanno, Tatiana Sousa Cunha
Health Care for Women International.2021; 42(11): 1279. CrossRef - Association of Baseline Characteristics With Insulin Sensitivity and β-Cell Function in the Glycemia Reduction Approaches in Diabetes: A Comparative Effectiveness (GRADE) Study Cohort
Neda Rasouli, Naji Younes, Kristina M. Utzschneider, Silvio E. Inzucchi, Ashok Balasubramanyam, Andrea L. Cherrington, Faramarz Ismail-Beigi, Robert M. Cohen, Darin E. Olson, Ralph A. DeFronzo, William H. Herman, John M. Lachin, Steven E. Kahn, Jill P. Cr
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(2): 340. CrossRef - Sex/Gender Differences in Obesity Prevalence, Comorbidities, and Treatment
Ashley J. Cooper, Sapana R. Gupta, Afaf F. Moustafa, Ariana M. Chao
Current Obesity Reports.2021; 10(4): 458. CrossRef - Age-, sex- and ethnicity-related differences in body weight, blood pressure, HbA1c and lipid levels at the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes relative to people without diabetes
Alison K. Wright, Paul Welsh, Jason M. R. Gill, Evangelos Kontopantelis, Richard Emsley, Iain Buchan, Darren M. Ashcroft, Martin K. Rutter, Naveed Sattar
Diabetologia.2020; 63(8): 1542. CrossRef - Impact of Gender on Type II Diabetes Glycemic and Cardiovascular Markers Control and Treatment
Khaled A. Alswat
Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences.2020; 23(12): 1643. CrossRef - Preadipocytes of obese humans display gender-specific bioenergetic responses to glucose and insulin
Michaela Keuper, Lucia Berti, Bernhard Raedle, Stephan Sachs, Anja Böhm, Louise Fritsche, Andreas Fritsche, Hans-Ulrich Häring, Martin Hrabě de Angelis, Martin Jastroch, Susanna M. Hofmann, Harald Staiger
Molecular Metabolism.2019; 20: 28. CrossRef - Risk of all-cause and CHD mortality in women versus men with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Guodong Xu, Dingyun You, Liping Wong, Donghui Duan, Fanqian Kong, Xiaohong Zhang, Jinshun Zhao, Wenhua Xing, Liyuan Han, Li Li
European Journal of Endocrinology.2019; 180(4): 243. CrossRef - Gut flora, diet and intestinal metabolism on cardiovascular risk
Deepak Bhatnagar
Current Opinion in Lipidology.2015; 26(2): 148. CrossRef
- Diabetes and cardiovascular risk according to sex: An overview of epidemiological data from the early Framingham reports to the cardiovascular outcomes trials

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





